|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Chondroid Lipoma Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
 |
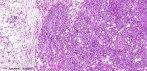
Chondroid lipoma is a rare, benign variant of lipomatous tumour. It was first reported by Meis and Enzinger in 1993. Age and sex: Chondroid lipoma occurs predominantly in the third decade of life, mostly in females (female-male ratio, 4:1). Site: These are usually located in the subcutaneous tissue, superficial muscular fascia, or skeletal muscles, especially in proximal limbs and limb girdles. Gross: Encapsulated and lobulated mass usually about 4 cm in maximal dimension. Microscopic features: The tumour is composed of a varying admixture of eosinophilic multivacuolated cells arranged in strands, nests and sheets together with mature adipocytes. These are present in a myxoid and chondroid-like stroma. Multivacuolated cells contain contain fat and glycogen (demonstrated by periodic acid Schiff and Oil-red-O stains) and may resemble chondroblasts or hibernoma cells. There may be areas of fibrosis and hemosiderin deposition. There is little pleomorphism and mitotic activity is low. Immunohistochemistry: Usually Vimentin and S 100 protein positive (strongly in adipocytes, weakly in lipoblasts.) CD68 and cytokeratins may be positive in some cases. EMA is negative. MIB1 proliferation index less than 1%. Cytogenetics: Revealed a balanced translocation t (11,16) (q13; p12 -13). Differential Diagnosis: 1. Myxoid liposarcoma - Characterized by a plexiform vascular network and higher cellularity with true lipoblasts. 2.Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma - Tumour is more lobulated with fibrous septa and presence of a thin peripheral capsule. There is absence of adipocytes and lipoblasts. Tumoral chondroblasts are more round and have few or no intracytoplasmic vacuoles. 3. Extraskeletal chondroma - Located in the distal extremities, multinucleated giant cells and true cartilaginous areas are present. There are no intracytoplasmic fat vacuoles. 4. Mixed tumor -There are foci of epithelial differentiation, lipoblasts are absent. Note: If the pathologist is unaware of the entity he may consider a sarcoma either of adipose tissue - a round cell liposarcoma - or of cartilage- an extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma.
|
|
|
 |