|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Hidradenoma Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
 |
| Syn: Clear cell hidradenoma,
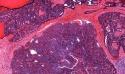
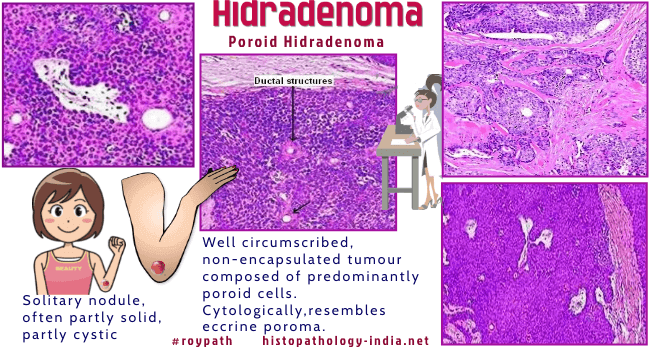
solid and cystic hidradenoma or dermal acrospiromas. Hidradenoma is a benign dermal appendage tumour. Hidradenomas may be of eccrine or apocrine origin. Solitary, nodule often partly solid, partly cystic. Site: Located in any part of the body. There is a slight predilection for the head, face, and upper extremities.
Differential diagnosis: It is sometimes difficult to distinguish solid cellular hidradenomas without duct-like structures and glomus tumour without a vascular pattern. Clear cell hidradenoma: Differential Diagnosis- Clear cell tumours of skin ; Hidradenocarcinoma. (Clear cell hidradenoma: a mimic of metastatic clear cell tumors). Nodular hidradenoma can recur after inadequate excision.
|
|
|
 |