|

Custom Search
|
|
Infectious Disease Online Pathology of Poliomyelitis
|
|
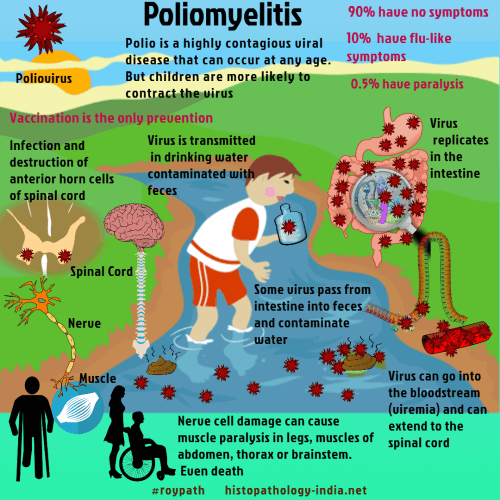
Poliomyelitis is an acute infection by polioviruses. Most infections are asymptomatic, but when the virus invades the central nervous system it destroys lower motor neurons, causing paralysis. Sporadic infections may be seen at any time, but outbreaks occur mostly in summer. More recent epidemics have stricken adults as well as children. Polio was sporadic in earlier centuries, but later became epidemic and subsequently pandemic. The incidence peaked during the 1950s in many developed countries. Immunization have stopped its spread in the Western world, but polio remains a major public health problem in many developing countries. Poliovirus is transmitted in drinking water contaminated with feces. The virus replicates in the mucosa of the small intestine. Some virions pass from there into the feces, contaminating water and completing the cycle. Others enter the bloodstream (viremia) and extend to the spinal cord, where they infect and destroy the anterior horn cells, causing paralysis.
|
Further reading: Vaccine-derived poliomyelitis 12 years after infection in Minnesota. MRI findings in an infant with vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis. |
|
|