|

Custom Search
|
|
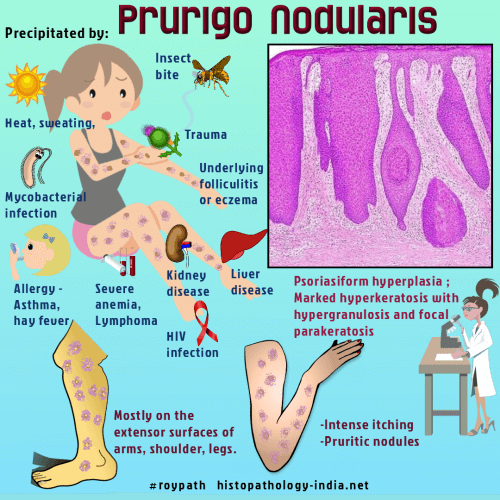
Dermpath-India Pathology of Prurigo Nodularis "Skin lesion characterized by Pseudo-Epitheliomatous Hyperplasia"
|
|
Prurigo nodularis is an uncommon lesion that presents as extremely pruritic nodules with a wide anatomical distribution but particularly on extensor aspects of limbs. Often lesions are multiple but solitary nodules can occasionally occur. Lesions tend to be symmetrical and are associated with excoriations. Females are more often affected than males. Many authors consider this condition as part of the spectrum of lichen simplex. Atypical mycobacteria may be a contributing factor in prurigo nodularis.
Differential diagnosis: Diagnosis is not difficult if the biopsy is big enough. In small biopsies differential diagnosis include Keratoacanthoma and other causes of pseudo-epitheliomatous hyperplasia. Note: Pseudoepitheliomatous (pseudocarcinomatous) hyperplasia : This is a benign pathological reaction pattern, histologically characterized by bulbous thickening of squamous epithelium (follicular infundibula and acrosyringium). There is abrupt transition beween lesion and adjacent epidermis. The cells have abundant often glassy cytoplasm. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is seen in the following conditions: Chronic irritation ; skin trauma ; dermal inflammatory processes like chromomycosis ; aspergillosis ; pyoderma, Prurigo nodularis ; Granuloma fissuratum and in associatiation with Chondrodermatitis Nodularis Chronica Helicis chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis ; Spitz nevus , melanoma, overlying granular cell tumour and cutaneous T cell tumour .
|
|
|


