|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Relapsing Polychondritis
|
| Relapsing
polychondritis is a rare episodic and progressive inflammatory
disease of presumed autoimmune etiology first described in
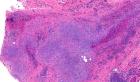
1923. Relapsing polychondritis affects cartilage in multiple organs, such as the ear, nose, larynx, trachea,bronchi, and joints. In addition, it can affect proteoglycan-rich tissues, such as the eyes, aorta, heart, and skin. Auricular chondritis, with red ears resembling infectious cellulitis, is the most common initial finding. There is redness and swelling of the cartilaginous ear, followed by cartilage inflammation elsewhere in the body. Antibodies to type II collagen in cartilage are found, and the earlobes are classically spared. Chronic disease may result in a flabby, droopy ear, cauliflower ear, or saddle nose deformity. Acute involvement of the tracheal cartilage may cause collapse of the airway with obstruction and pulmonary infections. Arthritis may be oligoarticular or polyarticular, most often involving the costochondral junctions. Other manifestations include audiovestibular damage; heart valve disease; and neurologic, ocular, and renal disease.
Histologically there is a mixed inflammatory infiltrate (lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, occasional eosinophils) extending into cartilage. Interface between cartilage and adjacent soft tissue is blurred. Cartilage demontrates loss of normal basophilia, loss of chondrocytes and destruction of lacunar architecture.
|
|
|