|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Spindle Cell Hemangioma (Haemangioendothelioma) Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
|
Spindle cell
hemangioma (hemangioendothelioma) is a distinct vascular lesion which was
initially considered to be a low grade angiosarcoma when
first described in 1986.
Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma. A low-grade angiosarcoma resembling a cavernous hemangioma and Kaposi's sarcoma. In recent years it has been suggested that spindle cell hemangioma is probably a vascular malformation or the lesion results from abnormalities of local blood flow. Spindle cell hemangioma may be associated with anomalies such as Mafucci's syndrome, Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome, lymphedema and early onset varicose vein. Treatment consists of
wide local excision without adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Clinical presentation:
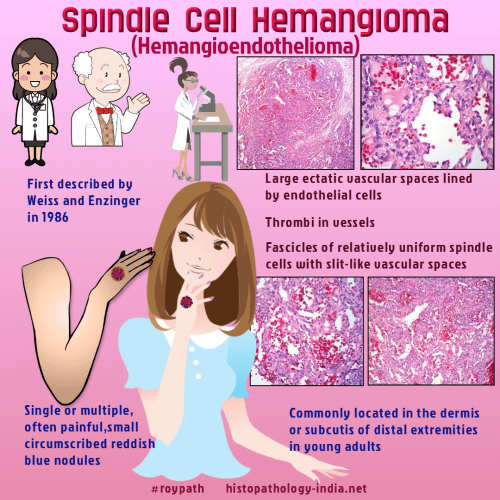
These lesions usually present as a single or multiple, often
painful, small circumscribed
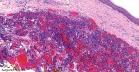
reddish blue nodules. Microscopic features: Microscopically this poorly circumscribed lesion consists of three main components: - Vascular component displaying gaping thin-walled vessels containing organizing thrombi (features resemble Cavernous hemangioma). - Solid area of spindle cells together with slit like vascular spaces (features resemble Kaposi's Sarcoma).
- Plump endothelial cells. Some of these cells contain vacuoles or intracytoplasmic lumina. Immunohistochemistry: The spindle cells are immunonegative for endothelial marker CD34 . Most of these spindle cells stain positively for Vimentin and some cells are positive for actin and desmin. Differential diagnosis: Unlike Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma the spindle cells in Kaposi's sarcoma stain positively for CD34.
|
|
|