|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Clear Cell Acanthoma "Skin lesion with enlarged pale stained keratinocytes" Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
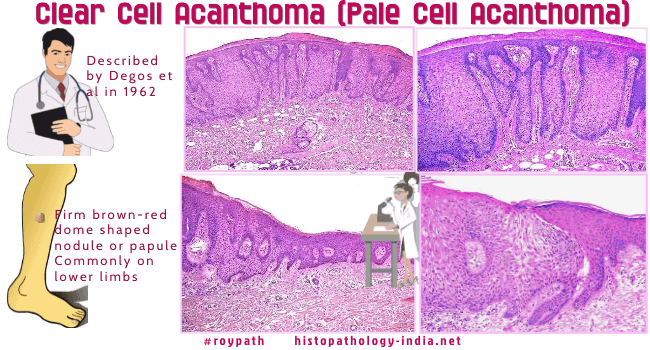
Clear cell acanthoma (pale cell acanthoma) is a discrete idiopathic psoriasiform lesion of large pale staining, non-keratinizing, glycogenated, monomorphous keratinocytes associated with neutrophils. The lesion is separated from the adjacent epidermis. It was first described by Degos et al in 1962. Clinical presentation: Presents as a firm brown-red dome shaped nodule or papule. The lesion is usually between 5 to 10 mm or more in diameter. Clear cell acanthoma is usually solitary but can be multiple. Clinical bleeding is rare. The surface of the lesion may be smooth to bosellated and crusted. Age: Middle aged and elderly individuals. Some cases have been reported in younger patients. Site: Commonly located on the lower limbs. These may also be found on the trunk and face.
Immunohistochemistry: The cells contain cytokeratin and involucrin but not carcinoembryonic antigen.
Differential diagnosis: Eccrine poroma ; Trichilemmoma ; Psoriasis; Clonal type-Seborrheic keratosis ; Verruca vulgaris
|
|
|