|

Custom Search
|
| Dermpath-India Pathology of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
|
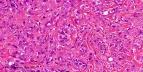
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is a malignant vascular tumour. The tumour occupies an intermediate position in the spectrum of epithelioid vascular tumours lying between the benign epithelioid hemangioma and the more aggressive epithelioid angiosarcoma. Site: Soft tissue, lung ( formerly known as intravascular bronchioalveolar tumour), pleura, liver, peritoneum, bone, lymph nodes and skin. Age: Middle-aged adults. Microscopic features: Poorly defined and infiltrative tumour, characterized by nests and cords of spindle to epithelioid cells embedded in a hyaline, myxoid, chondroid or collagenous stroma. Diagnostic feature: The cells show prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles. Red blood cells may be present within some of these vacuoles (reminiscent of primitive vascular channels). These vacuoles are mucin negative. Other features that may be present : Abundant osteoclast-like giant cells ; dystrophic calcification; metaplastic ossification. There is a low mitotic activity and mild to moderate pleomorphism. In some cases there are solid nests of tumour cells displaying cytological atypia together with increased mitotic activity (more than 1 per 10 HPF) and areas of necrosis. Cases with these features are associated with bad prognosis. Variant: Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27(1):48-57 Immunohistochemistry: Tumour cells express endothelial markers : CD31 is one of the most sensitive immunohistochemical markers. von Willibrand factor is also positive. Some cases show positivity for smooth muscle actin and cytokeratin. Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) is negative unlike other epithelial tumours. S-100 protein is also negative. The tumour has a good overall prognosis but local recurrences and distant metastases can develop. Differential diagnosis : Primary or metastatic carcinoma ; Epithelioid sarcoma (Positive for keratin, EMA and often CD34 ; Negative for CD31 or von Willibrand factor); Myxoid liposarcoma (branching vascular pattern and small multivacuolated lipoblasts) ; Myxoid chondrosarcoma (lobular architecture; absence of cytoplasmic vacuoles and S-100 protein positive). Characteristic morphological features together with appropriate immunohistochemical staining helps in establishing the diagnosis.
|
|
|
Copyright © 2022 histopathology-india.net