|

Custom Search
|
|
Infectious Disease Online Pathology of Rotavirus Diarrhea
|
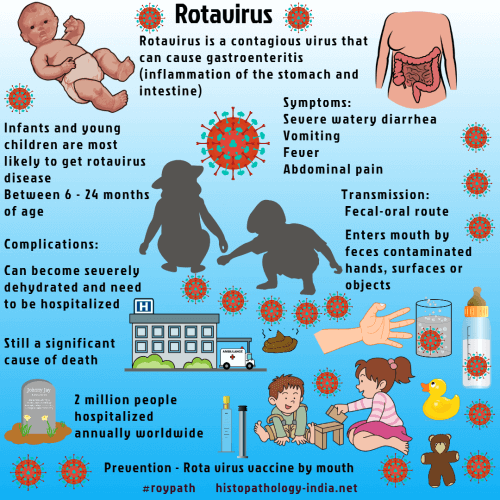
Rotaviruses contain double-stranded RNA, resemble a wheel, have icosahedral symmetry, and are “double-shelled” (with inner and outer capsid).Rotavirus particles have been found in the duodenal mucosa of children with acute gastroenteritis and in diarrheal stool specimens.In developed countries rotavirus is the most common pathogen of childhood diarrhea. Rotavirus-induced diarrhea is an endemic problem throughout the world, the organisms being identified in half the children in developing countries. In temperate countries rotavirus diarrhea usually has a seasonal winter peak, but in tropical countries high rates are observed throughout the year. Nosocomial infections are common, and shedding of rotavirus has been found in some (usually asymptomatic) newborns in communal obstetric nurseries within 3 to 4 days of birth. Antibodies to the rotavirus in colostrums and breast milk protect against infection. The highest incidence of symptomatic infection is in children aged 7 to 24 months. Most children have rotavirus antibodies by end of the third year, and nearly all infections in adults are subclinical. Rotavirus is spread by faecal-oral transmission, typically by person-to-person or by contact with a contaminated object. Contaminated water may be an important mode of transmission in developing countries. After an incubation period of 2 to 3 days there is an abrupt onset of watery diarrhea,followed by dehydration and vomiting and fever distinguish rotavirus diarrhea from diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli or Vibrio cholerae. Visit: Norovirus related diarrhea ; Cholera The upper respiratory tract may also be affected. In some countries, children have a self-limited illness that lasts for a few days. But coincidental infection with pathogenic enterobacteria may extend the duration. Severe life-threatening dehydration may be an important cause of mortality among children under 2 years of age. Although Rota virus infection is not associated to specific dermatologic clinical pictures, recently, different clinical manifestations have been reported in association with this infection. They include exanthema, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, and Acute Infantile Hemorrhagic Edema. The condition can be diagnosed microbiologically with stool cultures. The prognosis is excellent in healthy, immunocompetent individuals. Treatment of rotavirus diarrhea consists of prompt intravenous or oral rehydration.
|
|
|
Copyright © 2022 histopathology-india.net

