|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Sebaceoma Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
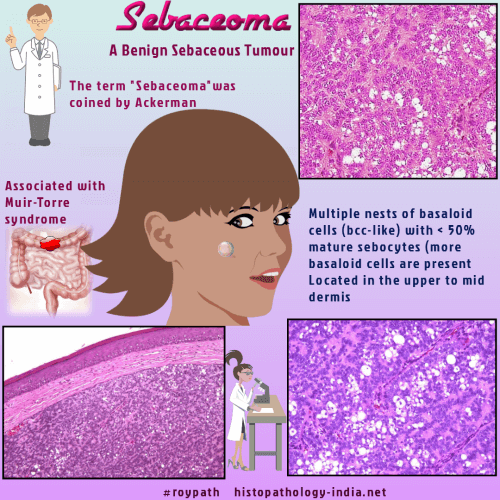
| Troy and Ackerman
defined the term sebaceoma as benign neoplasm of basaloid cells
with varying numbers of mature sebocytes.
(Sebaceoma.
A distinctive benign neoplasm of adnexal epithelium differentiating
toward sebaceous cells.
Am J
Dermatopathol. 1984 Feb;6(1):7-13 ) Distinction between sebaceous adenoma and sebaceoma may be difficult and there is an increasing tendency to regard these two tumours as part of a continuum of benign tumours. Some authors use the term sebaceous adenoma when half or less than 50% of the lesion is composed of germinative and transitional cells, and sebaceoma when greater than 50% of the lesion is composed of germinative and transitional cells. The term 'sebaceous epithelioma' has been largely discarded by many pathologists as the term 'epithelioma' is confusing & has been used in different ways by various pathologists. Clinical presentation: Presents as a solitary circumscribed nodule or an ill-defined plaque. May also present as multiple lesions, specially in Muir-Torre Syndrome. Site: Located on the face or scalp.
Differential Diagnosis: 1) Sebaceous Carcinoma- some cases of sebaceoma are difficult to differentiate reliably from carcinoma because of the germinative cells (mitotically active and may display atypical nuclear features) ; 2) Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation. The tumour usually does not recur after excision.
|
|
|
 |