|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Xanthelasma |
 |
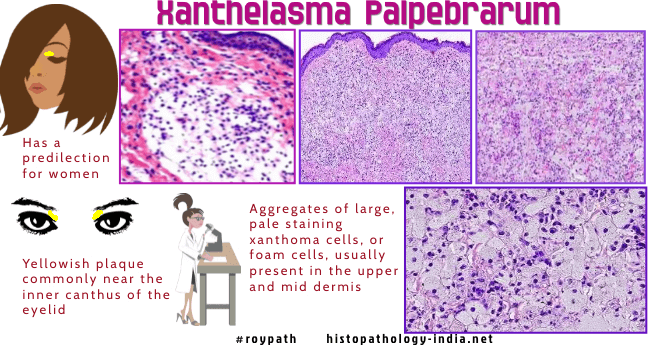
| Syn:
Xanthelasma Palpebrarum.
Xanthelasma is the most common form of xanthoma and is characterized by one or more yellowish plaques on the eyelid or in the periorbital skin. Most patients are in the 5th or 6th decade of life. The patients are often associated with atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. Lipid levels are normal in about 50% of the patients. In some young patients there is higher incidence of hypercholesterolemia. Alteration in apolipoprotein levels (A1 and B) in patients with xanthelasma may predispose to cutaneous and systemic deposition of lipids, including atherosclerosis. Patients irrespective of the size of the lesion or serum lipid levels should be screened using carotid intima media thickness for detection of subclinical atherosclerosis.
These lesions are usually removed for cosmetic reasons. Depth of tissue invasion of xanthelasma plays an important role in the selection of suitable surgical procedure. A careful clinical examination of the famous painting of Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci shows a yellow irregular spot at the inner end of the left upper eyelid and a 3 cm long well-circumscribed lump on the dorsum of the right hand beneath the index finger. According to several authors this is regarded as the first case of Xanthelasma. Related post: Verruciform Xanthoma
|
|
|
Visit:- Infectious Disease Online

|
Copyright © 2002-2022 histopathology-india.net