|

Custom Search
|
|
Dermpath-India Pathology of Rheumatoid Nodule Dr Sampurna Roy MD 2022
|
 |
|
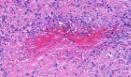
Rheumatoid nodules occur
in about 20-25% patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The presence of these extra-articular lesions correlates with the extent of joint involvement and they are an index of disease severity. They may also occur in rheumatic fever or rarely in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatoid nodules have also been reported in patients with no previous history of rheumatoid arthritis or any other systemic disease. 'Accelerated rheumatoid nodulosis' is a condition in which small nodules develop on the hand, feet and ears during methotrexate therapy. Age and sex : Rheumatoid nodules may develop in adults and in children and is slightly more common in females. Location: These are usually situated near bony structures close to a joint. The lesions are primarily located in the subcutaneous tissue and may involve deep and superficial dermis. Gross: Fibrous white masses with creamy yellow irregular areas of necrobiosis. The size varies from a few millimeters to centimeters.
Differential diagnosis: Deep variant of granuloma annulare: Contains abundant mucin (appears pale and basophilic) surrounded by palisades of histiocytes. Clinical information is very useful. There is degeneration of collagen in early lesion. Thickened collagen bundles are present in old lesions. Tiers of inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells) are present throughout the reticularis dermis. Inflammatory cells & histiocytes are present in the septa of subcutaneous fat.
|
|
|
 |